Benjamin Franklin once said, "An investment in knowledge still pays the best interest."
This also applies if you invest in stocks. You have an advantage if you know how stock markets perform.
This works out?
Of course!
The business cycle shows where the global economy is.
The first step is to understand the business cycle. Along with sector rotation, you improve your investment decisions.
What is an economic cycle? – Definition
The fluctuations in economic activity are called the business cycle or economic cycle. After a period of upswing, there follows a downturn (recession), which ends in depression.
These wave-like movements can be represented, for example, with fluctuations in gross domestic product and other indicators.
Understand business cycles
Business cycles are like ebb and flow. They come and go. They are an integral part of the global economy.
These are the four typical business cycle phases:
Expansion (Boom)
Recession (Downturn)
Depression (Trough)
Recovery
Metrics that influence these four economic phases are inflation-adjusted or real gross domestic product (GDP), industrial production, unemployment figures, income, corporate sales and central bank interest rates. All of these metrics are used to describe the official definition of the current business cycle.
One misconception is that a recession is defined as two consecutive quarters of declining real GDP. That would be too easy and not always right. In particular, the recessions of 1960–1961 and 2001 do not involve two consecutive quarters of contracting real GDP.
Since the USA is one of the largest industrialized countries in the world and most of the economic data is collected there, a look at the US business cycle is very important. Because this also influences Germany.
For this reason, I have specialized in identifying US economic cycles to determine the right sector for investing and trading.
What is a recession?
A recession is a vicious cycle. Gradual declines in industrial production, higher unemployment, lower incomes and reduced sales are leading to a further decline in industrial production, which is spreading rapidly from industry to industry and region to region.
This is a domino effect, which is why the spread of a local recession often ends in a global recession.
What is an economic boom?
An economic boom is a positively accelerating whirlpool of rising industrial production and corporate profits, followed by rising incomes and rising sales. This then leads to an increase in production.
This domino effect means that an economic upswing is self-propelled and can last for several years.
Measurement and timing of business cycles
Everyone determines business cycles differently.
I use the inloopo Business Cycle Tool with the US Leading Economic Index from the US Conference Board. The tool shows me the current economic cycle on a monthly basis.
inloopo business cycle tool with US Leading Economic Index (LEI)
![[caption ]Picture of the [inloopo Economic Cylcle Tool](https://www.inloopo.com/economic-cycle/)](https://images.ctfassets.net/wejpe8yzflc3/3jvJHIdgtw9Asehg2N9Hmx/84ec6dc75426935fad82cce14939888e/Economic_cycle_with_Leading_Economic_Indicator__LEI_en.jpg)
This leading economic indicator is based on 10 fundamental business cycle indicators that enable economic activity to be described 6 to 10 months in advance.
In contrast to the simplified model in the first figure, 5 possible economic phases are defined for the exact determination:
Decline (recession)
Recovery
Early growth (early boom)
Late growth (late boom)
Rebound (Special Phase)
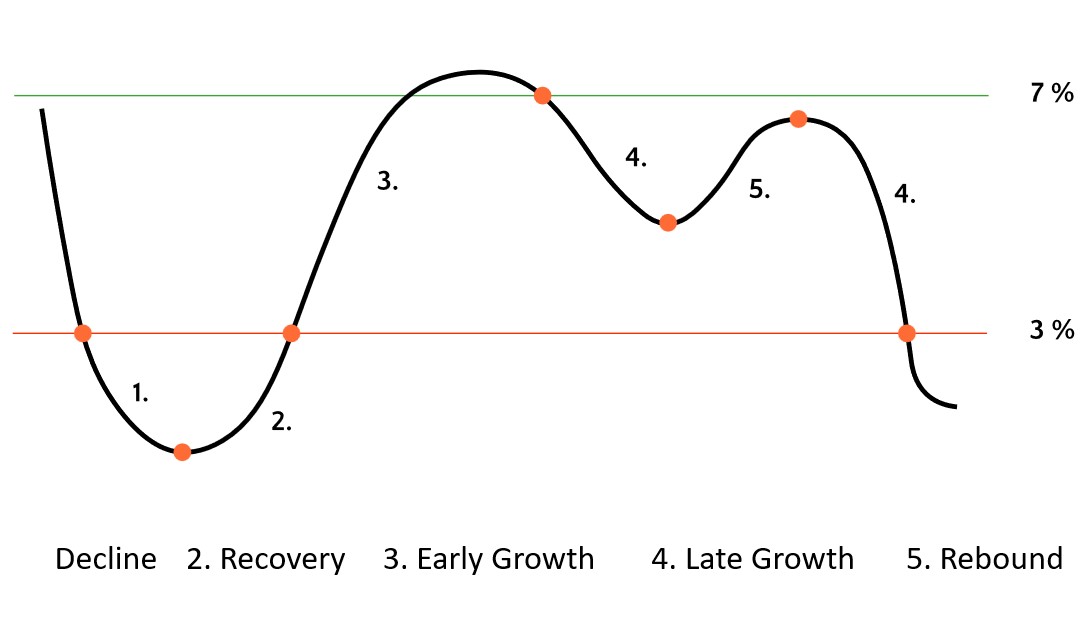
With the help of the US Leading Economic Index, the beginning and end of each phase can be precisely determined.
Why do I define 5 economic phases?
I use a fifth phase because history has shown that there is a phase between late growth and recession. This is the bounce phase. This phase is mostly determined by a tighter monetary policy of the central banks with rising interest rates.
Statistically, the utilities and technology sectors are the least affected by central bank policy. Therefore, these two sectors are preferred by investors who are looking for above-average share price developments.
Each economic phase is therefore determined by monetary policy or other economic factors and there are 1 to 3 sectors in each phase that can outperform the overall market (S&P 500 Index).
And that's exactly what I'm about.
With just a few transactions per year and investing in the right sectors that outperform the overall market, investment risk is minimized while delivering a better return.
To prove that this strategy works over the past 20 years, I ran a back test. You can find the results in the separate blog article "Results of sector rotation with ETFs".
Current business cycle
You can find the current business cycle in my free tool on the current business cycle.
How long does an economic cycle last?
The duration of any business cycle depends on many factors and does not follow a fixed time.
As you can see from the Leading Economic Index, for example, the overall length of each cycle is quite different. The last three business cycles have been:
May 2009 - May 2020: 11 years in total
November 2001 – May 2009: 7 years and 6 months in total
In 2023 we are in a new economic cycle.
I'm curious how long this will last. 😊
What was the longest business cycle?
2009 to 2020 was the longest business cycle so far at 11 years (source).
Summary
Super!
You have now not only learned which economic phases there are, but also how to determine the current phase.
And all with the analysis of a single indicator, the US Leading Economic Index.
This is possible because this indicator is based on 10 fundamental economic indicators.
This method saves you a lot of time and work. Like at the grocery store, when you buy a 12-pack of beers for the price of one. Have you seen anything like this before? 😉
In my next article I will show you the results of the inloopo sector rotation strategy.
Stay tuned.
